Theories of International Mobility and the Incorporation of Immigrants
Class 3: Determinants of Migration II
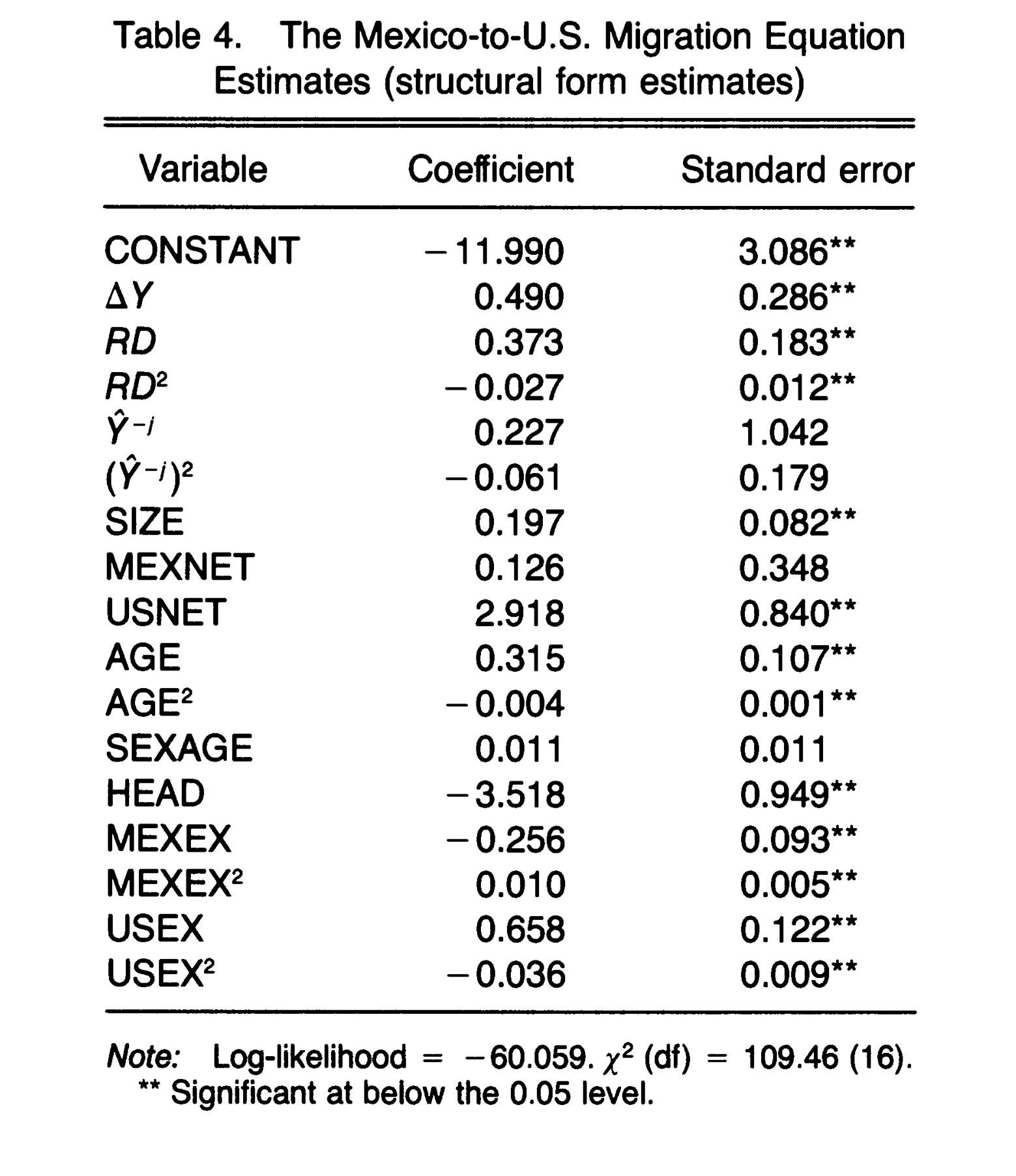
Massey & Garcia España 1987
- Where is gender in this?
- What are the costs of migration?
- Is enforcement considered empirically?
- Would we see same results today?
- What about macro level?
- Does it matter how close the connections are?
Massey & Garcia España 1987
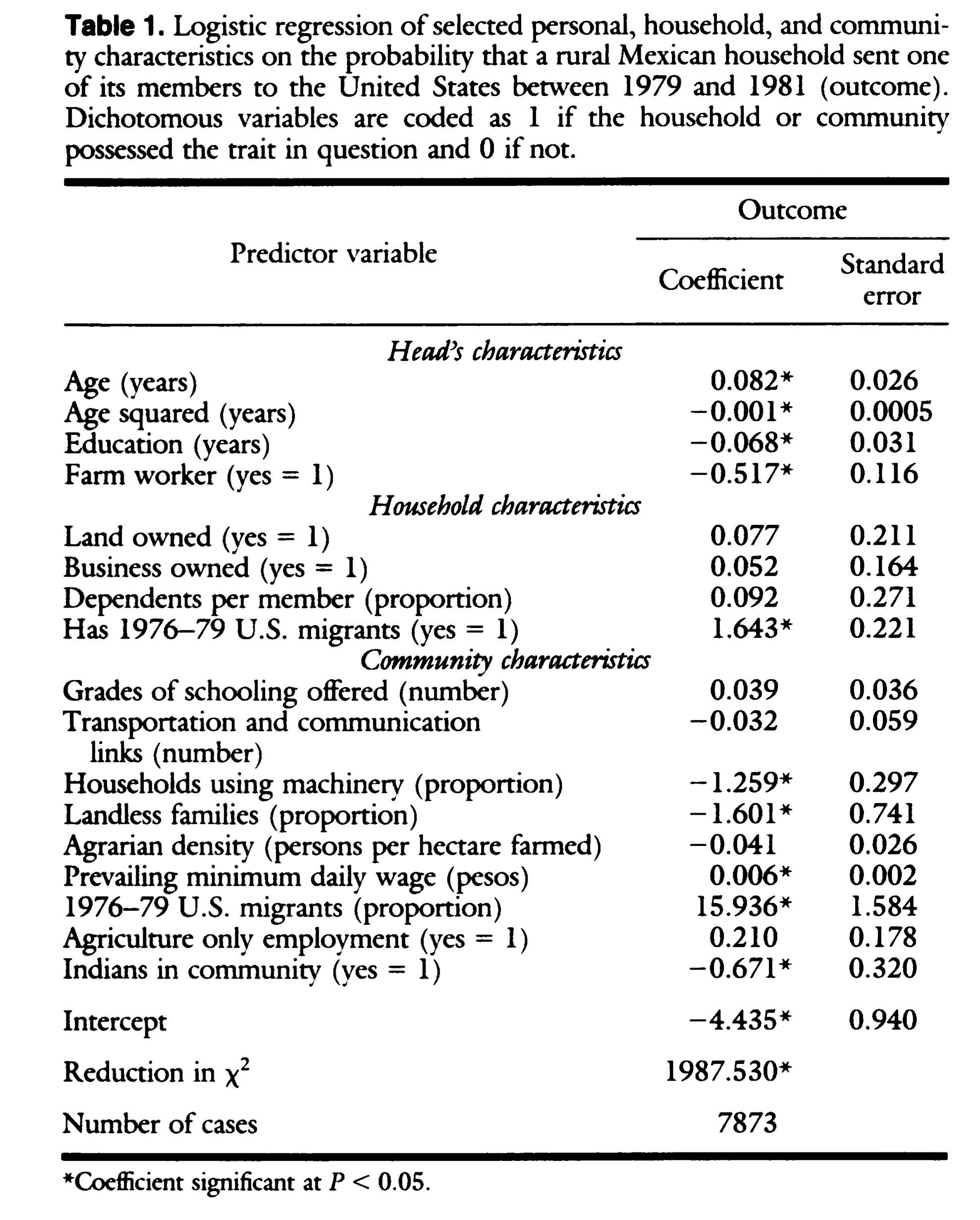
Massey & Garcia España 1987
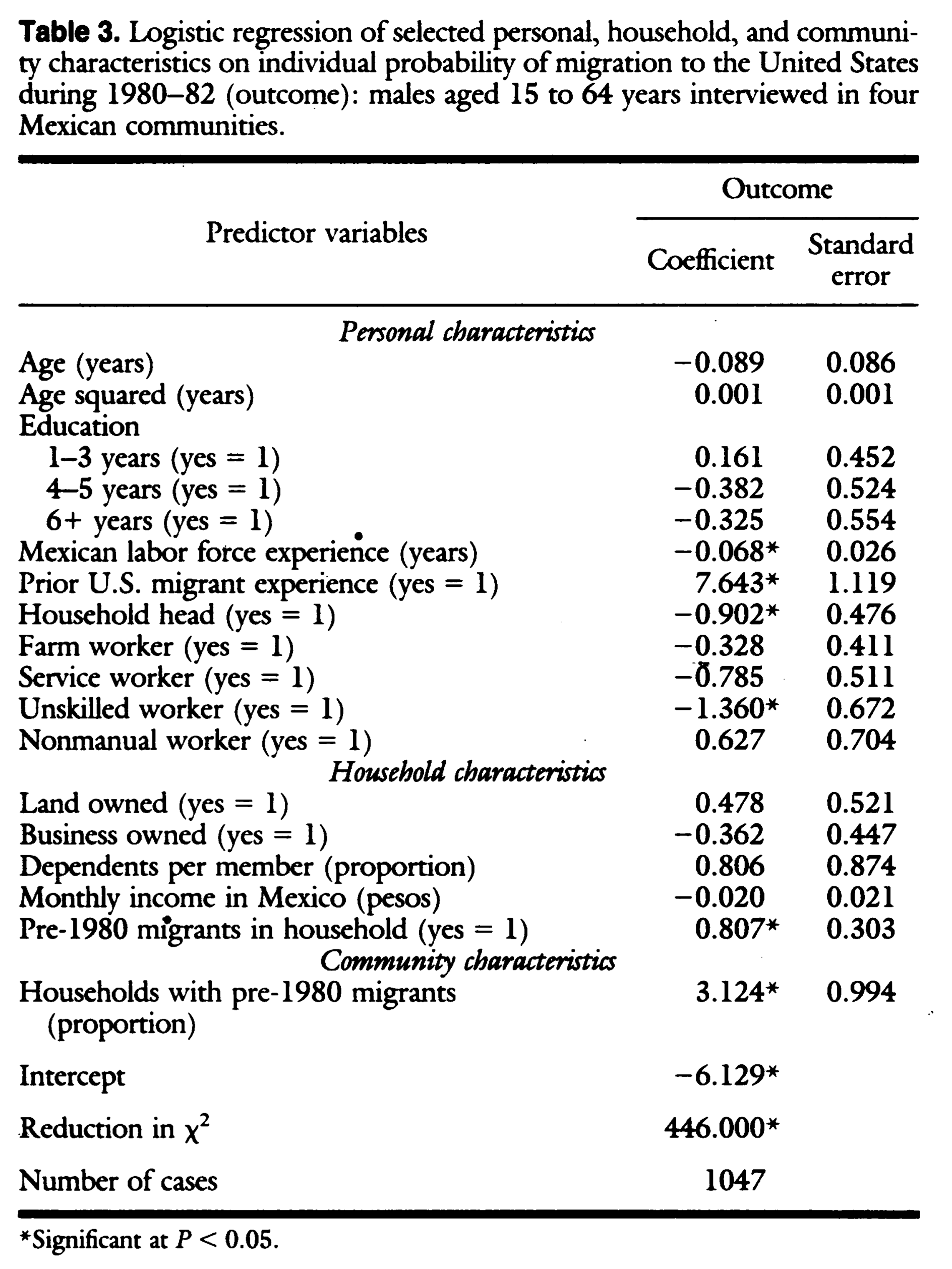
Massey & Garcia España 1987
$$P=\frac{1}{1+e^{bx}}$$Neoclassical Theory
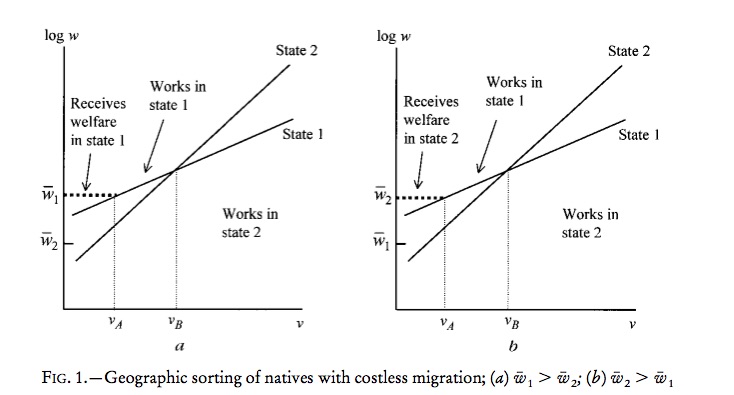
Borjas (1999)
Earnings Function
$$\log w_0 = \mu_0 + \eta_0v$$$$\log w_j = \mu_j + \eta_jv$$
New Economics of Labor Migration
Whereas owners of production inputs or commodities . . . can ordinarily ship them away . . . while themselves staying put, owners of labor must usually move along with their labor.
- Oded Stark & David E. Bloom, The New Economics of Labor Migration, American Economic Review (1985).
Furthermore, owners of labor have both feelings and independent wills.
- Oded Stark & David E. Bloom, The New Economics of Labor Migration, American Economic Review (1985).
Relative Deprivation
Stark & Taylor 1989
- Do intragroup comparisons affect perception, incentives, evaluation, and behavior?
- Village A family incomes: 20, 30, 40, 50, 60
- Village B family incomes: 20, 60, 65, 70, 75, 80
Stark & Taylor 1989
- Person is relatively deprived of X when:
- does not have X
- sees another person as having X
- wants X
- sees it feasible to have X
Stark & Taylor 1989